In brief
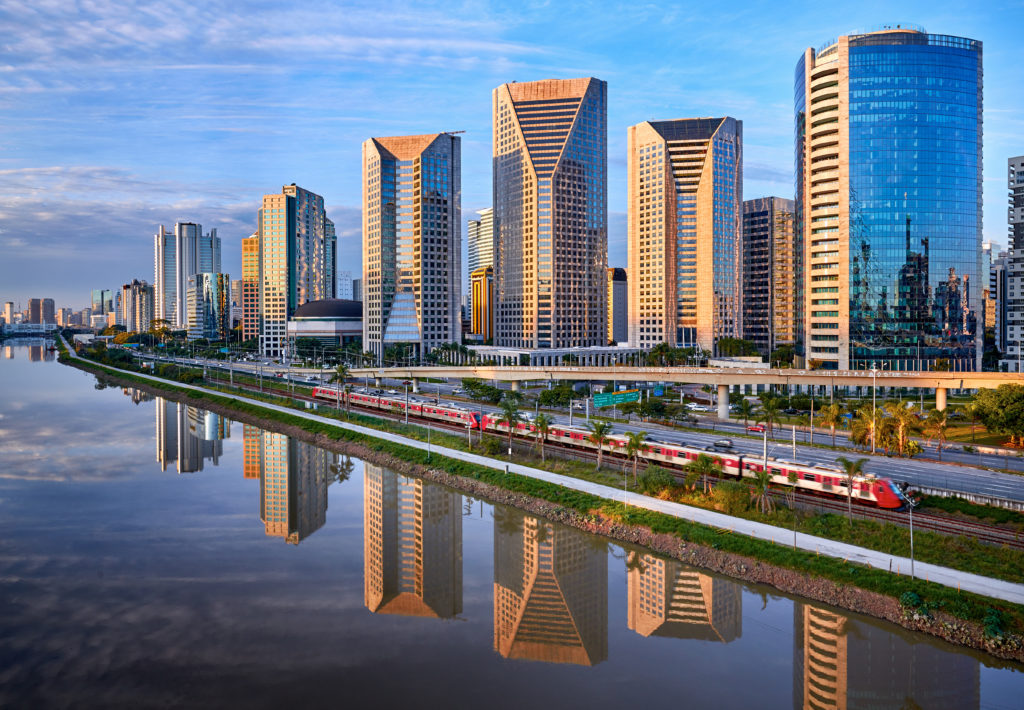
On 6 May 2024, the Federal Government published Federal Law No. 14.852/2024, which established the Legal Framework for the Electronic Games Industry in Brazil. The new law will regulate the manufacture, import, marketing, development, and commercial use of electronic games in the country.
More details
Federal Law No. 14.852/2024 sets out the basic principles and rules for the development and sale of electronic games in Brazil. It establishes guidelines on the manufacture, import, marketing, development and commercial use of electronic games, in addition to providing that the State must establish the indicative age classification. Therefore, it provides a specific framework for this sector in Brazil and ensures the protection of its consumers and users.
The Legal Framework for the Electronic Games Industry establishes the principles and guidelines for the sector. These include recognizing the sector as a vector for economic, social, environmental, and cultural development; safeguarding consumers (especially children and teenagers) in the electronic games environment; and ensuring privacy, protecting personal data, and promoting user self-determination.
The new law also provides for the use of electronic games beyond entertainment, i.e., for educational purposes in school environments, therapeutic purposes, training purposes in institutional environments, as well as for media and advertising purposes.
The law also specifies that the management and operation of electronic games must be based on the best interests of children and teenagers and ensure that the systems developed do not foster or create an environment conducive to violence, exploitation and any kind of discrimination or neglect. In addition, the new law points to the need to implement measures that guarantee universal design and accessibility for children and teenagers with disabilities when accessing electronic games.
In addition, the conception, design, management and operation of electronic games accessed by children and teenagers must be based on the interests of this age group, and games with interaction must guarantee the application of safeguards, such as a system for receiving complaints.
It will be up to the State to establish the indicative age classification of games, taking into account the risks related to digital purchases in the context of games, which can stimulate unbridled consumption in children.
As for taxation aspects, Federal Law No. 14.852/2024 stipulates that: (i) the electronic games industry will have incentives similar to those applicable to the cultural sector under the Rouanet Law – which aims to incentivize cultural activities in Brazil – and the Audiovisual Law – that aims to incentivize the national movie industry; (ii) the government will regulate customs clearance and import taxes for games, with a view to fostering innovation in the sector; and (iii) individual entrepreneurs and individual micro-entrepreneurs (MEIs) who develop electronic games will have special treatment (which will be regulated at a later date).
* * * * *

Trench Rossi Watanabe and Baker McKenzie have executed a strategic cooperation agreement for consulting on foreign law.